广度优先遍历与最短路径
广度优先遍历从某个顶点 v 出发,首先访问这个结点,并将其标记为已访问过,然后顺序访问结点v的所有未被访问的邻接点 {vi,..,vj} ,并将其标记为已访问过,然后将 {vi,...,vj} 中的每一个节点重复节点v的访问方法,直到所有结点都被访问完为止。
我们可以分为三个步骤:
- (1)使用一个辅助队列 q,首先将顶点 v 入队,将其标记为已访问,然后循环检测队列是否为空。
- (2)如果队列不为空,则取出队列第一个元素,并将与该元素相关联的所有未被访问的节点入队,将这些节点标记为已访问。
- (3)如果队列为空,则说明已经按照广度优先遍历了所有的节点。
下图所示,右边蓝色表示从 0 开始遍历节点的顺序,下面是记录距离 0 的距离,可知广度优先遍历能求出无权图的最短路径。
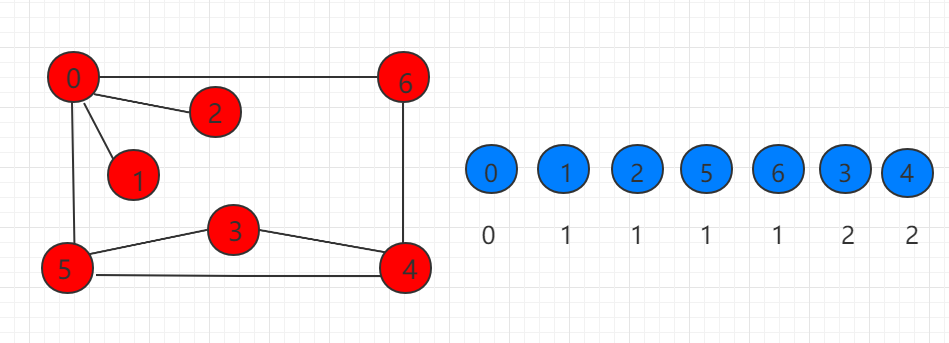
下面用代码展示如何用广度优先遍历方式完成遍历,并且查询到最短路径。我们在上一小节代码的基础上增加一全局变量 ord 数组,记录路径中节点的次序。ord[i] 表示 i 节点在路径中的次序。同时构造函数做出相应调整,在遍历相邻节点时 每访问一个未被访问的节点进行 ord[i] = ord[v] + 1记录距离。邻接表的广度优先遍历时间复杂度为 O(V+E),邻接矩阵的时间复杂度为O(V^2)。
...
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从s点到其他点的路径
public ShortestPath(Graph graph, int s){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert s >= 0 && s < G.V();
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
from = new int[G.V()];
ord = new int[G.V()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
ord[i] = -1;
}
this.s = s;
// 无向图最短路径算法, 从s开始广度优先遍历整张图
LinkedList<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.push( s );
visited[s] = true;
ord[s] = 0;
while( !q.isEmpty() ){
int v = q.pop();
for( int i : G.adj(v) )
if( !visited[i] ){
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
from[i] = v;
ord[i] = ord[v] + 1;
}
}
}
...
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从s点到其他点的路径
public ShortestPath(Graph graph, int s){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert s >= 0 && s < G.V();
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
from = new int[G.V()];
ord = new int[G.V()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
ord[i] = -1;
}
this.s = s;
// 无向图最短路径算法, 从s开始广度优先遍历整张图
LinkedList<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.push( s );
visited[s] = true;
ord[s] = 0;
while( !q.isEmpty() ){
int v = q.pop();
for( int i : G.adj(v) )
if( !visited[i] ){
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
from[i] = v;
ord[i] = ord[v] + 1;
}
}
}
...
查看从 s 点到 w 点的最短路径长度,若从 s 到 w 不可达,返回-1。
...
public int length(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.V();
return ord[w];
}
...
public int length(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.V();
return ord[w];
}
...
Java 实例代码
源码包下载:Download
src/runoob/graph/ShortestPath.java 文件代码:
package runoob.graph;
import runoob.graph.read.Graph;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.Vector;
/**
* 广度优先遍历与最短路径
*/
public class ShortestPath {
// 图的引用
private Graph G;
// 起始点
private int s;
// 记录dfs的过程中节点是否被访问
private boolean[] visited;
// 记录路径, from[i]表示查找的路径上i的上一个节点
private int[] from;
// 记录路径中节点的次序。ord[i]表示i节点在路径中的次序。
private int[] ord;
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从s点到其他点的路径
public ShortestPath(Graph graph, int s){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert s >= 0 && s < G.V();
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
from = new int[G.V()];
ord = new int[G.V()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
ord[i] = -1;
}
this.s = s;
// 无向图最短路径算法, 从s开始广度优先遍历整张图
LinkedList<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.push( s );
visited[s] = true;
ord[s] = 0;
while( !q.isEmpty() ){
int v = q.pop();
for( int i : G.adj(v) )
if( !visited[i] ){
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
from[i] = v;
ord[i] = ord[v] + 1;
}
}
}
// 查询从s点到w点是否有路径
public boolean hasPath(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.V();
return visited[w];
}
// 查询从s点到w点的路径, 存放在vec中
public Vector<Integer> path(int w){
assert hasPath(w) ;
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
// 通过from数组逆向查找到从s到w的路径, 存放到栈中
int p = w;
while( p != -1 ){
s.push(p);
p = from[p];
}
// 从栈中依次取出元素, 获得顺序的从s到w的路径
Vector<Integer> res = new Vector<Integer>();
while( !s.empty() )
res.add( s.pop() );
return res;
}
// 打印出从s点到w点的路径
public void showPath(int w){
assert hasPath(w) ;
Vector<Integer> vec = path(w);
for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(vec.elementAt(i));
if( i == vec.size() - 1 )
System.out.println();
else
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
}
// 查看从s点到w点的最短路径长度
// 若从s到w不可达,返回-1
public int length(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.V();
return ord[w];
}
}
import runoob.graph.read.Graph;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.Vector;
/**
* 广度优先遍历与最短路径
*/
public class ShortestPath {
// 图的引用
private Graph G;
// 起始点
private int s;
// 记录dfs的过程中节点是否被访问
private boolean[] visited;
// 记录路径, from[i]表示查找的路径上i的上一个节点
private int[] from;
// 记录路径中节点的次序。ord[i]表示i节点在路径中的次序。
private int[] ord;
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从s点到其他点的路径
public ShortestPath(Graph graph, int s){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert s >= 0 && s < G.V();
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
from = new int[G.V()];
ord = new int[G.V()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
ord[i] = -1;
}
this.s = s;
// 无向图最短路径算法, 从s开始广度优先遍历整张图
LinkedList<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.push( s );
visited[s] = true;
ord[s] = 0;
while( !q.isEmpty() ){
int v = q.pop();
for( int i : G.adj(v) )
if( !visited[i] ){
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
from[i] = v;
ord[i] = ord[v] + 1;
}
}
}
// 查询从s点到w点是否有路径
public boolean hasPath(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.V();
return visited[w];
}
// 查询从s点到w点的路径, 存放在vec中
public Vector<Integer> path(int w){
assert hasPath(w) ;
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
// 通过from数组逆向查找到从s到w的路径, 存放到栈中
int p = w;
while( p != -1 ){
s.push(p);
p = from[p];
}
// 从栈中依次取出元素, 获得顺序的从s到w的路径
Vector<Integer> res = new Vector<Integer>();
while( !s.empty() )
res.add( s.pop() );
return res;
}
// 打印出从s点到w点的路径
public void showPath(int w){
assert hasPath(w) ;
Vector<Integer> vec = path(w);
for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(vec.elementAt(i));
if( i == vec.size() - 1 )
System.out.println();
else
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
}
// 查看从s点到w点的最短路径长度
// 若从s到w不可达,返回-1
public int length(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.V();
return ord[w];
}
}
