Python3 条件控制
Python 条件语句是通过一条或多条语句的执行结果(True 或者 False)来决定执行的代码块。
可以通过下图来简单了解条件语句的执行过程:
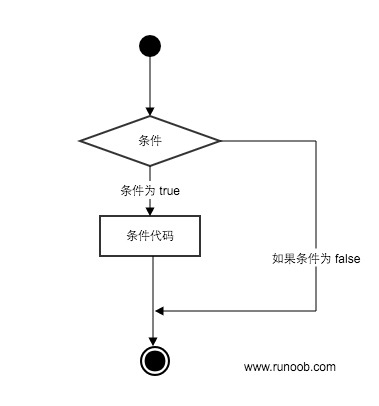
代码执行过程:
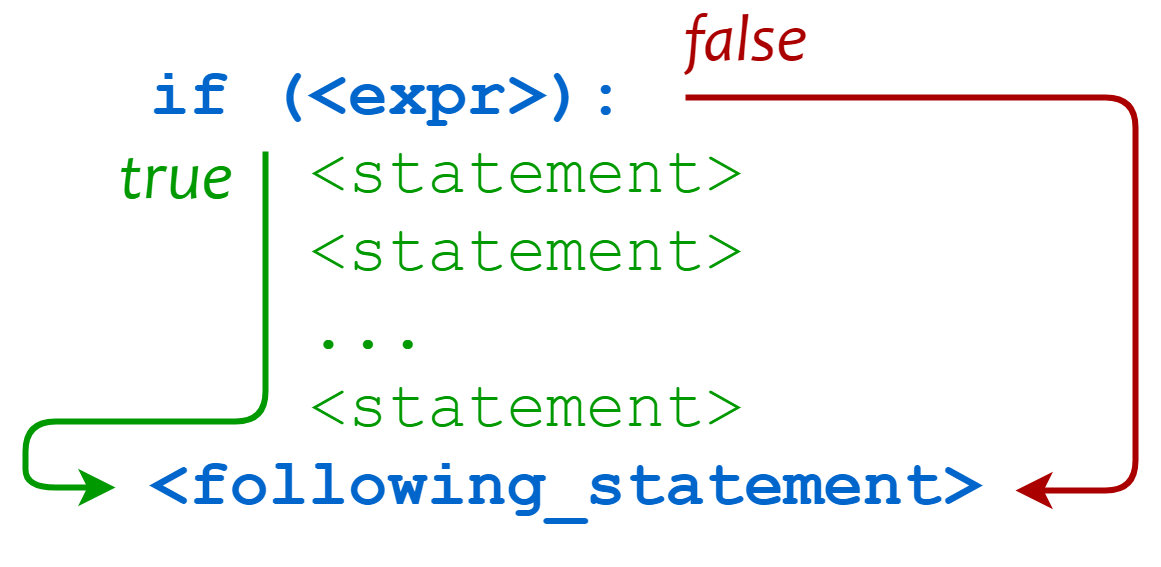
if 语句
Python中if语句的一般形式如下所示:
if condition_1:
statement_block_1
elif condition_2:
statement_block_2
else:
statement_block_3
- 如果 "condition_1" 为 True 将执行 "statement_block_1" 块语句
- 如果 "condition_1" 为False,将判断 "condition_2"
- 如果"condition_2" 为 True 将执行 "statement_block_2" 块语句
- 如果 "condition_2" 为False,将执行"statement_block_3"块语句
Python 中用 elif 代替了 else if,所以if语句的关键字为:if – elif – else。
注意:
- 1、每个条件后面要使用冒号 :,表示接下来是满足条件后要执行的语句块。
- 2、使用缩进来划分语句块,相同缩进数的语句在一起组成一个语句块。
- 3、在 Python 中没有 switch...case 语句,但在 Python3.10 版本添加了 match...case,功能也类似,详见下文。
Gif 演示:

实例
以下是一个简单的 if 实例:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python3
var1 = 100
if var1:
print ("1 - if 表达式条件为 true")
print (var1)
var2 = 0
if var2:
print ("2 - if 表达式条件为 true")
print (var2)
print ("Good bye!")
执行以上代码,输出结果为:
1 - if 表达式条件为 true 100 Good bye!
从结果可以看到由于变量 var2 为 0,所以对应的 if 内的语句没有执行。
以下实例演示了狗的年龄计算判断:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python3
age = int(input("请输入你家狗狗的年龄: "))
print("")
if age <= 0:
print("你是在逗我吧!")
elif age == 1:
print("相当于 14 岁的人。")
elif age == 2:
print("相当于 22 岁的人。")
elif age > 2:
human = 22 + (age -2)*5
print("对应人类年龄: ", human)
### 退出提示
input("点击 enter 键退出")
将以上脚本保存在dog.py文件中,并执行该脚本:
$ python3 dog.py 请输入你家狗狗的年龄: 1 相当于 14 岁的人。 点击 enter 键退出
以下为if中常用的操作运算符:
| 操作符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
< |
小于 |
<= |
小于或等于 |
> |
大于 |
>= |
大于或等于 |
== |
等于,比较两个值是否相等 |
!= |
不等于 |
实例
#!/usr/bin/python3
# 程序演示了 == 操作符
# 使用数字
print(5 == 6)
# 使用变量
x = 5
y = 8
print(x == y)
以上实例输出结果:
False False
high_low.py文件演示了数字的比较运算:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python3
# 该实例演示了数字猜谜游戏
number = 7
guess = -1
print("数字猜谜游戏!")
while guess != number:
guess = int(input("请输入你猜的数字:"))
if guess == number:
print("恭喜,你猜对了!")
elif guess < number:
print("猜的数字小了...")
elif guess > number:
print("猜的数字大了...")
执行以上脚本,实例输出结果如下:
$ python3 high_low.py 数字猜谜游戏! 请输入你猜的数字:1 猜的数字小了... 请输入你猜的数字:9 猜的数字大了... 请输入你猜的数字:7 恭喜,你猜对了!
if 嵌套
在嵌套 if 语句中,可以把 if...elif...else 结构放在另外一个 if...elif...else 结构中。
if 表达式1:
语句
if 表达式2:
语句
elif 表达式3:
语句
else:
语句
elif 表达式4:
语句
else:
语句
实例
# !/usr/bin/python3
num=int(input("输入一个数字:"))
if num%2==0:
if num%3==0:
print ("你输入的数字可以整除 2 和 3")
else:
print ("你输入的数字可以整除 2,但不能整除 3")
else:
if num%3==0:
print ("你输入的数字可以整除 3,但不能整除 2")
else:
print ("你输入的数字不能整除 2 和 3")
将以上程序保存到 test_if.py 文件中,执行后输出结果为:
$ python3 test.py 输入一个数字:6 你输入的数字可以整除 2 和 3
match...case
Python 3.10 增加了 match...case 的条件判断,不需要再使用一连串的 if-else 来判断了。
match 后的对象会依次与 case 后的内容进行匹配,如果匹配成功,则执行匹配到的表达式,否则直接跳过,_ 可以匹配一切。
语法格式如下:
match subject:
case <pattern_1>:
<action_1>
case <pattern_2>:
<action_2>
case <pattern_3>:
<action_3>
case _:
<action_wildcard>case _: 类似于 C 和 Java 中的 default:,当其他 case 都无法匹配时,匹配这条,保证永远会匹配成功。
实例
def http_error(status):
match status:
case 400:
return "Bad request"
case 404:
return "Not found"
case 418:
return "I'm a teapot"
case _:
return "Something's wrong with the internet"
mystatus=400
print(http_error(400))
以上是一个输出 HTTP 状态码的实例,输出结果为:
Bad request
一个 case 也可以设置多个匹配条件,条件使用 | 隔开,例如:
...
case 401|403|404:
return "Not allowed"
match...case 更多内容参考:Python match-case 语句
