正则表达式 - 断言
断言(Assertion)是正则表达式中用于指定匹配位置的元字符,它们不匹配任何实际字符,而是匹配字符之间的位置。
假设我们要在一篇长文中找到所有价格后面的数字,而不是找到所有的数字,普通的正则表达式可能会匹配到所有数字,但使用断言,你可以精确地指定:我只匹配那些紧跟在价格后面的数字。
本文将带你系统学习正则表达式中四种核心的断言:正向先行断言、负向先行断言、正向后行断言 和 负向后行断言。
断言的特点
- 零宽度:不占用匹配字符的位置
- 条件检查:只检查是否满足特定条件
- 不影响匹配结果:仅作为匹配的约束条件
实例
const regex = /foo(?=bar)/;
console.log(regex.test("foobar")); // true
console.log(regex.test("food")); // false
断言的类型
正则表达式中的断言主要分为两大类四种类型:
| 断言类型 | 正则语法 | 别称 | 检查方向 | 期望条件 | 通俗解释 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正向先行断言 | (?=pattern) |
正前瞻 | 向右(向前) | 存在 pattern |
我要找的位置,它的右边必须是... |
| 负向先行断言 | (?!pattern) |
负前瞻 | 向右(向前) | 不存在 pattern |
我要找的位置,它的右边一定不能是... |
| 正向后行断言 | (?<=pattern) |
正后顾 | 向左(向后) | 存在 pattern |
我要找的位置,它的左边必须是... |
| 负向后行断言 | (?<!pattern) |
负后顾 | 向左(向后) | 不存在 pattern |
我要找的位置,它的左边一定不能是... |
正向先行断言 (?=...)
正向先行断言 用于匹配这样一个位置:在这个位置之后(右边),必须紧跟着出现指定的模式 ...。
语法与参数
- 语法:
(?=pattern) - 作用:检查当前位置右侧是否匹配
pattern。如果匹配,则断言成功,引擎会回到当前位置继续后续匹配。 - 关键特性:零宽度,即它只检查,不"吃掉"任何字符。
pattern中的内容不会成为最终匹配结果的一部分。
代码示例 1:提取价格数字
假设我们有一串文本,需要提取所有价格:后面的金额数字。
实例:JavaScript
// 正向先行断言
// 匹配一个或多个数字,但要求右侧紧跟"元"
// "元"本身不参与匹配结果
const pattern = /\d+(?=元)/g;
const matches = text.match(pattern);
console.log("匹配到的价格数字:", matches);
// 输出:['299', '599', '20']
实例:Python
text = "商品A价格:299元,商品B价格:599元,运费:20元。"
# 使用正向先行断言
# 匹配一个或多个数字 (\d+),但要求这个数字的右边必须紧跟着"元"
# 注意:"元"本身不会被匹配到结果中
pattern = r'\d+(?=元)'
matches = re.findall(pattern, text)
print("匹配到的价格数字:", matches)
# 输出:匹配到的价格数字: ['299', '599', '20']
代码解析:
\d+是主表达式,匹配一个或多个数字。(?=元)是断言,它检查\d+匹配到的数字串的右侧是否紧跟着一个"元"字。- 引擎首先找到
299,然后向右看,发现是"元",断言成功,所以299被记录。 - 继续找到
599,右边是"元",成功,记录。 - 找到
20,右边是"元",成功,记录。最终,我们只得到了数字部分。
代码示例 2:验证复杂密码
要求密码必须包含至少一个大写字母、一个小写字母和一个数字。
实例:JavaScript
// 多个正向先行断言
const pattern = /^(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*\d).{8,}$/;
// ^ 字符串开始
// (?=.*[A-Z]) 右侧必须存在至少一个大写字母
// (?=.*[a-z]) 右侧必须存在至少一个小写字母
// (?=.*\d) 右侧必须存在至少一个数字
// .{8,} 总长度至少 8
// $ 字符串结束
return pattern.test(password);
}
// 测试数据
const passwords = ["Weak", "strong123", "STRONG123", "Strong123"];
passwords.forEach(pwd => {
console.log(`密码 '${pwd}' 是否有效:${validatePassword(pwd)}`);
});
// 输出:
// 密码 'Weak' 是否有效:false
// 密码 'strong123' 是否有效:false
// 密码 'STRONG123' 是否有效:false
// 密码 'Strong123' 是否有效:true
实例:Pyhton
def validate_password(password):
# 使用多个正向先行断言来分别检查条件
pattern = r'^(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*\d).{8,}$'
# ^ 代表字符串开始
# (?=.*[A-Z]) 断言:从当前位置(开头)向右看,必须能在任意字符(.*)后找到一个大写字母
# (?=.*[a-z]) 断言:同样从开头向右看,必须能找到一个小写字母
# (?=.*\d) 断言:从开头向右看,必须能找到一个数字
# .{8,} 主表达式:匹配任意字符至少8次(总长度要求)
# $ 代表字符串结束
if re.match(pattern, password):
return True
else:
return False
# 测试数据
passwords = ["Weak", "strong123", "STRONG123", "Strong123"]
for pwd in passwords:
print(f"密码 '{pwd}' 是否有效:{validate_password(pwd)}")
# 输出:
# 密码 'Weak' 是否有效:False # 长度不够,且缺数字
# 密码 'strong123' 是否有效:False # 缺大写字母
# 密码 'STRONG123' 是否有效:False # 缺小写字母
# 密码 'Strong123' 是否有效:True # 符合所有条件
负向先行断言 (?!...)
负向先行断言 与正向先行断言相反。它匹配一个位置,在这个位置之后(右边),不能紧跟着出现指定的模式 ...。
语法与参数
- 语法:
(?!pattern) - 作用:检查当前位置右侧是否不匹配
pattern。如果不匹配,则断言成功。 - 关键特性:同样是零宽度。
代码示例:查找非 ing 结尾的单词
在一句话中,找到所有不以 ing 结尾的单词。
实例:JavaScript
const text1 = "playing swimming run walk jumping sing";
const pattern1 = /\b\w+(?<!ing)\b/g;
console.log(text1.match(pattern1));
// ['run', 'walk', 'sing']
// 示例 2:匹配不以 q 结尾的单词(正确语义版)
const text2 = "I like faq apple Iraq you banana q";
const pattern2 = /\b\w*[^q\W]\b/g;
// 含义:
// [^q\W] 单词最后一个字符不是 q
// 比 (?!q) 更符合"结尾不是 q"的真实需求
console.log(text2.match(pattern2));
// ['I', 'like', 'apple', 'you', 'banana']
// 示例 3:匹配不以 .js 结尾的文件名
const files = "index.js app.ts config.json main.js readme.md";
const pattern3 = /\b\w+\.(?!js\b)\w+\b/g;
// 含义: \.(?!js\b) 点号后不能是 js
console.log(files.match(pattern3));
// ['app.ts', 'config.json', 'readme.md']
正向后行断言 (?<=...)
正向后行断言 用于匹配一个位置,在这个位置之前(左边),必须紧挨着出现指定的模式 ...。
注意:不是所有编程语言的正则引擎都支持后行断言,JavaScript 在 ES2018 后才完全支持,而 Python 的 re 模块支持。
语法与参数
- 语法:
(?<=pattern) - 作用:检查当前位置左侧是否匹配
pattern。如果匹配,则断言成功。 - 关键特性:零宽度。
pattern必须有固定长度(不能是*或+等可变长度量词,在某些实现中)。
代码示例:提取货币符号后的金额
提取美元或英镑符号后面的数字,但不包括符号本身。
实例:JavaScript
const text1 = "Price: $199, £89, ¥1200";
const pattern1 = /(?<=\$|£)\d+/g;
// 含义:
// (?<=\$|£) 左侧必须是 $ 或 £
// \d+ 匹配数字本身
console.log(text1.match(pattern1));
// ['199', '89']
// 示例 2:匹配冒号后面的数字
const text2 = "port:8080 pid:1234 uid:1000";
const pattern2 = /(?<=:)\d+/g;
// 左侧必须是 :
console.log(text2.match(pattern2));
// ['8080', '1234', '1000']
// 示例 3:匹配版本号中的次版本(主版本号后)
const text3 = "v1.2 v2.15 v10.3";
const pattern3 = /(?<=v\d+\.)\d+/g;
// 左侧必须是 v + 数字 + 点
console.log(text3.match(pattern3));
// ['2', '15', '3']
// 示例 4:匹配 @ 后面的用户名(不包含 @)
const text4 = "hello @alice and @bob_smith";
const pattern4 = /(?<=@)[a-zA-Z_]\w*/g;
console.log(text4.match(pattern4));
// ['alice', 'bob_smith']
// 示例 5:匹配中文"第 X 章"里的章节数字
const text5 = "第1章 第12章 第3章";
const pattern5 = /(?<=第)\d+(?=章)/g;
// 左右同时约束,更清晰
console.log(text5.match(pattern5));
// ['1', '12', '3']
负向后行断言 (?<!...)
负向后行断言 是正向后行断言的反面。它匹配一个位置,在这个位置之前(左边),不能紧挨着出现指定的模式 ...。
语法与参数
- 语法:
(?<!pattern) - 作用:检查当前位置左侧是否不匹配
pattern。 - 关键特性:零宽度,通常要求
pattern为固定长度。
代码示例:查找非负整数
在一段文本中,匹配所有不是负数的整数(即,左边没有负号 - 的数字)。
实例:JavaScript
// 负向后行断言(lookbehind)
// 匹配数字,但要求左侧不能是负号 -
const pattern = /(?<!-)\b\d+\b/g;
const matches = text.match(pattern);
console.log("非负整数:", matches);
// 输出:['3', '22']
// -5、-1 左侧是 '-',断言失败,不匹配
综合应用与流程图
为了更直观地理解四种断言的工作流程,我们可以用下面的流程图来表示一个包含多种断言的复杂匹配过程:
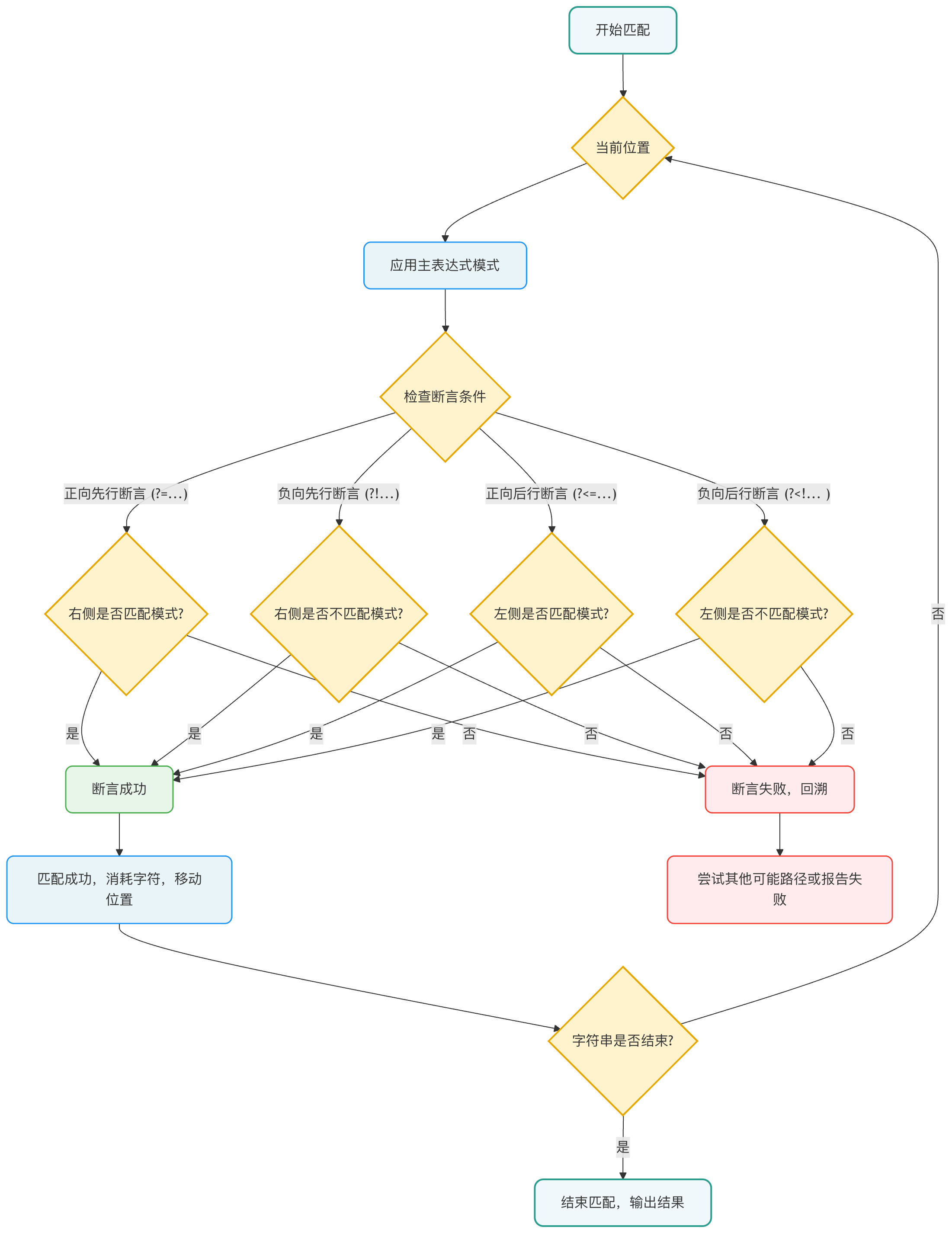
流程图说明:该图展示了正则表达式引擎在匹配时如何处理断言。核心在于,断言是一个独立的检查节点。引擎在主表达式尝试匹配的当前位置,根据断言类型,向左或向右检查上下文。只有所有断言条件都满足,匹配才能继续向下进行,并"消耗"字符;否则,引擎会回溯尝试其他可能性或宣告匹配失败。
